WSUS Settings for Windows 10/11
- Avijit Dutta

- Jul 31, 2025
- 3 min read
Updated: Aug 12, 2025
Published on: July 31, 2025
Author: Avijit Dutta
Category: Windows 10/11 | Microsoft | IT Infrastructure | Patch Management

💡 Introduction - WSUS Settings for Windows 10/11
In enterprise environments, WSUS (Windows Server Update Services) helps IT admins control Windows updates by delivering them from a local server. However, remote or hybrid users may not always have access to the corporate WSUS server. That's where "dual scan" or fallback to internet updates becomes important.
This blog covers WSUS Settings for Windows 10/11 systems along with fallback settings to Microsoft Update using:
✅ Windows Registry (with detailed key/value explanation)
✅ Group Policy (with setting-by-setting breakdown)
✅ PowerShell to verify configuration
🔧 Method 1: Configure via Windows Registry (Regedit)
📍 Registry Path
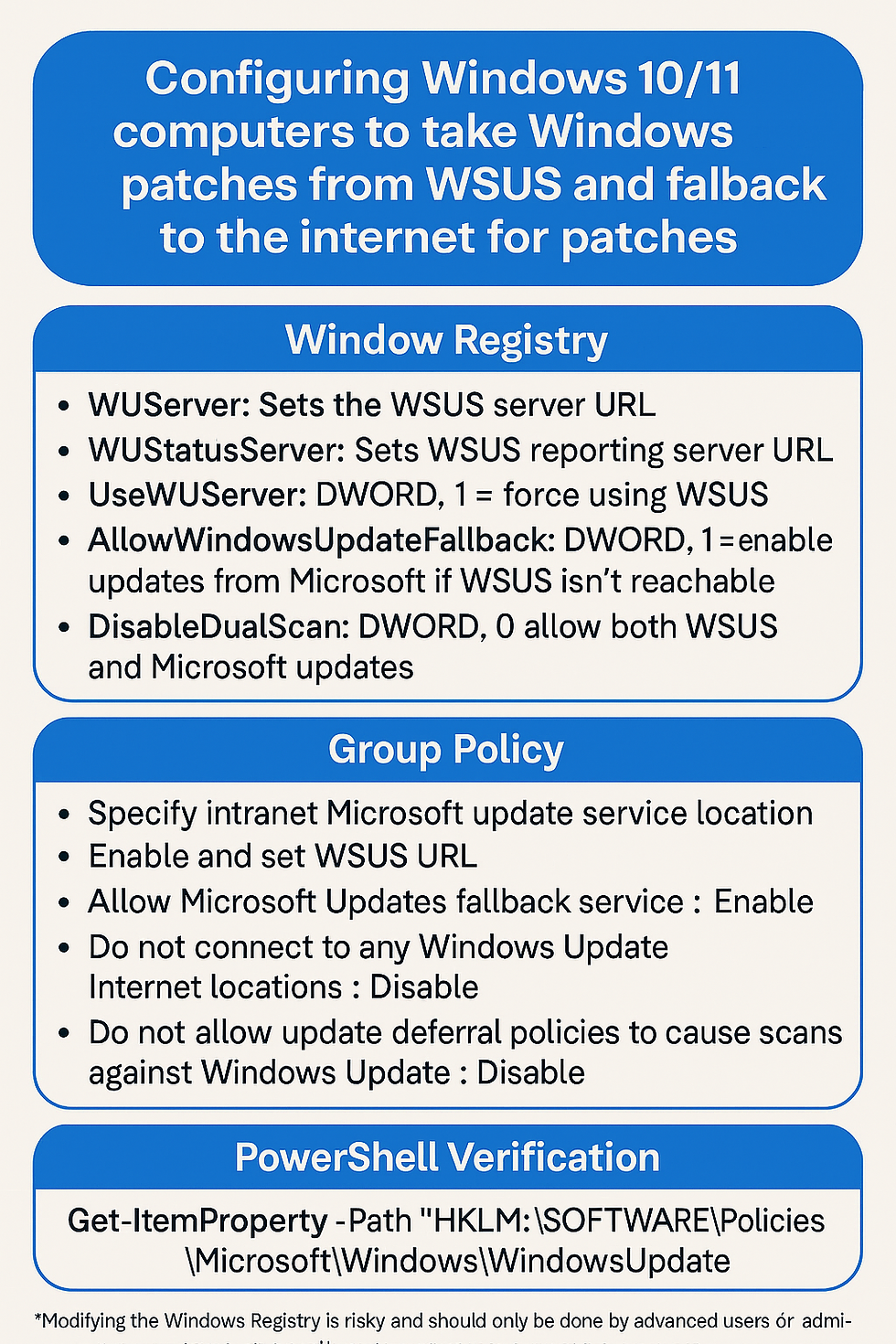
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\WindowsUpdateRegistry Entry | Type | Value | Description |
WUServer | String | http://your-wsus-server:8530 | Sets the WSUS server URL. |
WUStatusServer | String | http://your-wsus-server:8530 | Sets the WSUS reporting server URL. |
UseWUServer | DWORD | 1 | Forces the client to use WSUS. |
AllowWindowsUpdateFallback ⚠️ | DWORD | 1 | Enables fallback to Microsoft Update if WSUS is not reachable (requires 20H2+). |
DisableDualScan | DWORD | 0 | Allows dual scanning (WSUS + Microsoft Update). Set to 0 to enable dual scan. |
ElevateNonAdmins (Optional) | DWORD | 1 | Allows non-admins to scan/install updates. |
🛑 Registry Disclaimer: Editing the Windows Registry incorrectly can cause serious system issues. Always back up the registry and consult your system administrator before making changes.
🛡️ Method 2: Configure via Group Policy (Recommended for Enterprises)
📍 GPO Path:
Computer Configuration > Administrative Templates > Windows Components > Windows UpdatePolicy Name | Recommended Setting | Description |
Specify intranet Microsoft update service location | Enabled → WSUS URL | Set both download and status URLs. Example: http://your-wsus-server:8530 |
Allow Microsoft Updates fallback service (NEW) | Enabled | Lets device go to Windows Update if WSUS is down. |
Do not connect to any Windows Update Internet locations | Disabled | Must be disabled to allow fallback. |
Specify source service for specific classes | Not Configured | Don’t restrict unless using custom Update Management. |
Do not allow update deferral policies to cause scans against Windows Update | Disabled | Ensures scans don’t bypass WSUS. |
🔗 For more info, refer to Microsoft’s official documentation.
💻 PowerShell Command to Verify WSUS Settings
# Verify WSUS configuration and fallback eligibility
Get-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\WindowsUpdate"
# Check if fallback is allowed
(Get-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\WindowsUpdate").AllowWindowsUpdateFallback✅ If AllowWindowsUpdateFallback is 1, fallback to Microsoft Update is enabled.
✅ Use Get-WindowsUpdateLog to analyse update activity.
💡 Tips and Tricks for IT Admins
✅ Always test on pilot devices before mass rollout.
🔄 Use GPO Backup/Restore to quickly clone policies across OUs.
🔐 Use RSOP.msc or gpresult to verify if GPOs are being enforced.
☁️ Consider Azure Update Manager or Intune for modern update scenarios.
🌐 Combine with Delivery Optimisation for bandwidth savings.
🖨️ Printable One Page Poster
Your quick reference guide — ready to print and pin!
✅ Conclusion
By configuring Windows 10/11 to use WSUS as the primary update source with a Microsoft Update fallback, organisations can balance centralised control with reliability for remote/hybrid users.
Whether done through Group Policy or Registry, this approach ensures your endpoints remain secure, even when disconnected from corporate networks.
If you liked this article, do share the same. You can also buy me a Coffee using PayPal at "paypal.me/duttaavijit". This is purely a volunteer effort. THANK YOU !!!



Comments